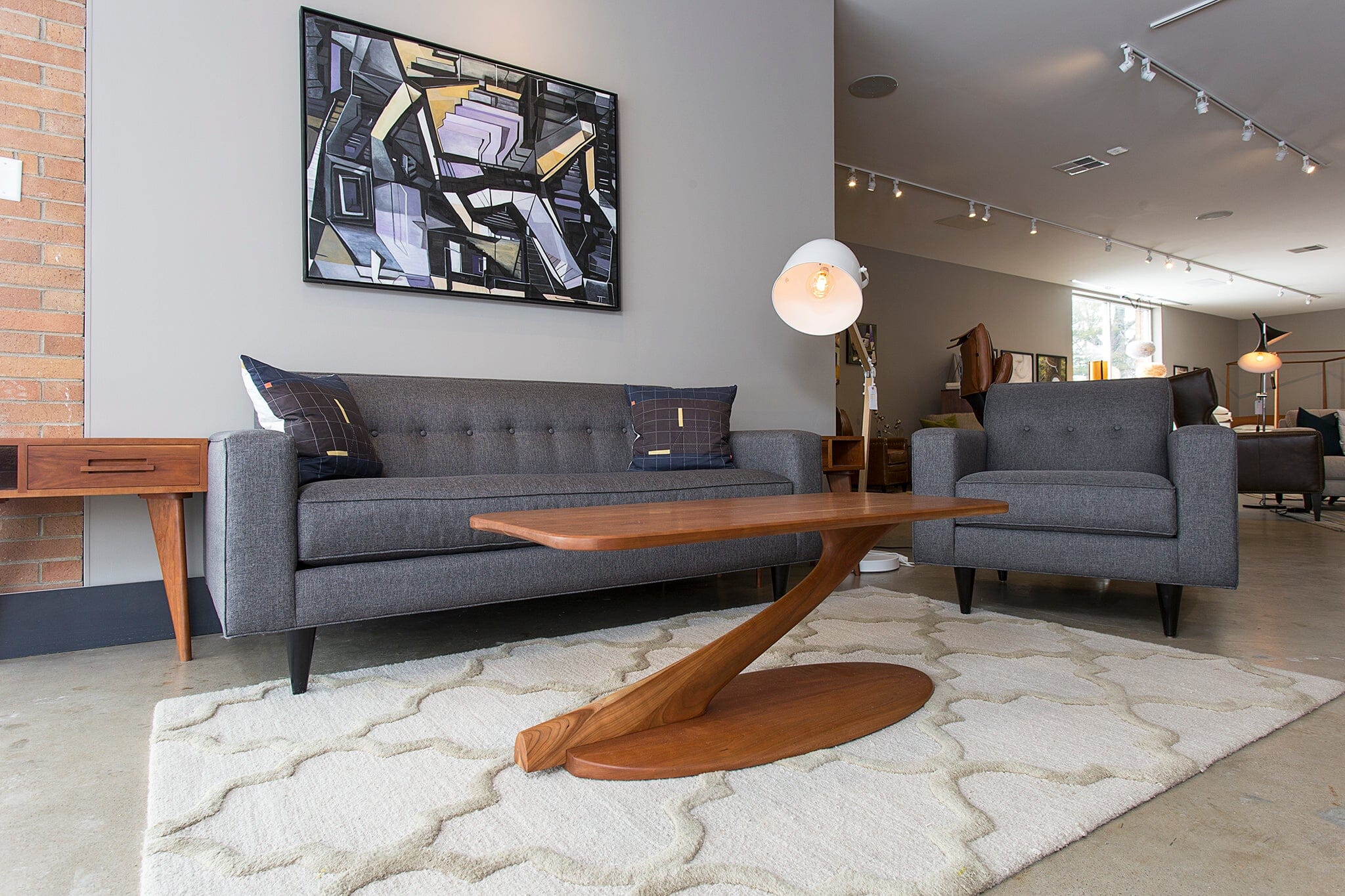
Maple is among the sought-after American hardwoods, boasting incredible strength and density. Despite being a tough timber, it’s surprisingly easy to mold and shape, making it a top choice among furniture makers.
Now, when people in the industry say maple, they generally refer to sugar maple. Aside from its durability, sugar maple is sought-after because of its light and creamy appearance, a versatile color to match any home.
There’s so much more you need to know about maple and why it’s a great material to use for furniture.
Types of Maple
Maple is not a single tree species. It’s the broad and common word for a diverse family of trees and shrubs called Acer.
Under the genus Acer are 132 unique “maple” species, many of which are found in Asia and some scattered across Europe, northern Africa, and North America. Popular maple species include:
- Sugar maple (Acer saccharum)
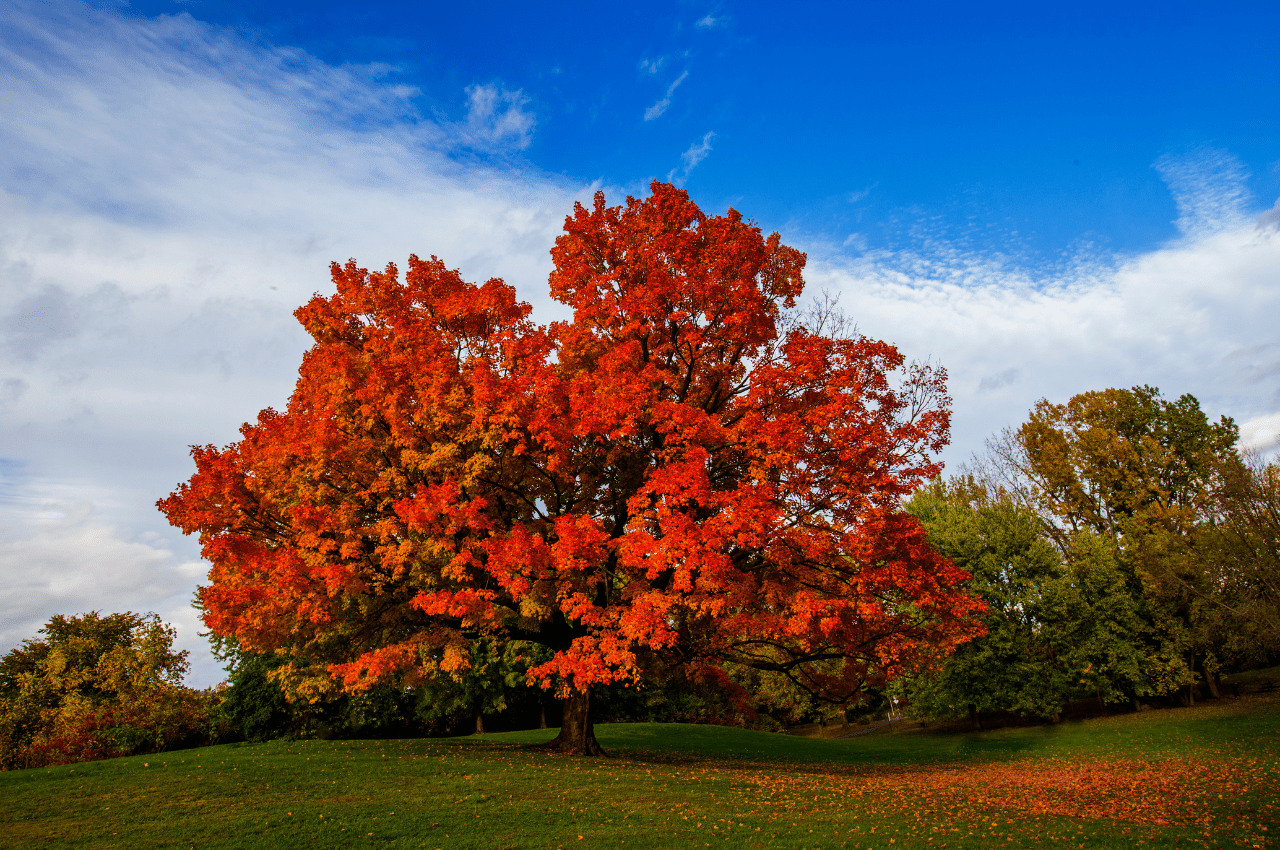
Common in the northeastern United States, the sugar maple tree (also called rock maple) is best known for producing maple syrup. It’s a stunner in the fall when its bright green leaves turn to a lovely mix of red, yellow, and orange. This tree can reach anywhere between 80 to 110 feet tall.
- Bigleaf maple (Acer macrophyllum)
The Bigleaf maple is a species native to the Pacific Northwest region of North America and one of the few commercially available hardwoods on the west coast. This species grows into an enormous tree, reaching up to 150 feet in height.
- Red maple (Acer rubrum)
Red maple is a common maple tree in North America and grows in urban (common landscape trees) and forest areas. Its leaves on top are green, but underneath, they appear silver. During autumn, the leaves turn bright red, giving the tree its name. It’s not as tall as the other maples and typically grows to about 50 feet tall when fully mature.
- Silver maple (Acer saccharinum)
Silver maple grows quickly and is commonly planted as shade trees. While this tree grows quickly (and tall, at about 80 feet when mature), it is brittle and prone to breaking, and its roots are shallow. The undersides of its leaves are soft silver, and the fall color is typically a pale yellow.
- Black maple (Acer saccharum ssp. nigrum)
The black maple is a subspecies of sugar maple native to the midwestern United States. It has a rounded crown and dense foliage in the fall that turns a beautiful golden yellow. It grows to about 65 feet and withstands most growing conditions, even in cold climates.
Hard Maple vs. Soft Maple
Hard maple refers to Sugar Maple and Black Maple trees and is a popular choice for flooring, furniture, cabinets, and even baseball bats. Soft maple trees, including red maple, boxelder, silver maple, and bigleaf maple, are commonly used for veneers, crates, and home woodenware due to their soft and lightweight wood.
As timber, soft maple trees look similar to hard maple. One way to tell them apart is to weigh them. Hard maple is often heavier and denser, although this test isn’t always accurate.
Defining Traits of Sugar Maple
T.Y. Fine Furniture uses various sustainable, high-quality hardwoods, mainly Oak, Walnut, Cherry, and Maple. For our maple furniture, we only use Sugar Maple or Black Maple to ensure that our pieces last for generations.
So, for the rest of this article, we’ll focus on Sugar Maple.
Maple wood is a popular choice for woodworkers and furniture enthusiasts due to its strong and durable nature, beautiful creamy color, and smooth grain pattern, making it ideal for staining.
Color
The sapwood of a Sugar Maple tree can vary from white to cream, sometimes with hints of gold, while the heartwood is typically a shade of reddish brown. Other trees are valued for their heartwood. But with sugar maple, it’s the sapwood that furniture makers usually choose due to its light and creamy color.
As hardwoods age, they experience a change in color due to exposure to oxygen and sunlight. This process causes light-colored woods like maple to darken over time, with the cream hue transitioning to a darker shade resembling honey or light gold.
Hardness
Hard maple species like Sugar Maple and Black Maple have the highest Janka Hardness Scale rating of any other maple species. Their hardness level reaches 1,450 lbf Janka, while soft maple species have a rating of about 700 to 950.
On the Janka Hardness Scale, Sugar Maple falls somewhere in the middle. It is less dense than Oak and slightly denser than Cherry.
Grain Pattern
The sugar maple has a range of grain patterns. It typically has a straight grain, but there are other variations, such as the Bird’s Eye pattern. This pattern features sporadic “eyes” throughout the wood, providing a nice accent.
Other styles of figured maple (a term used to describe unique patterns on timber that are often caused by injury and disease) include blister, curly, burl, fiddle back, and spalted.
Depending on our stock, we may have maple wood with curly or bird’s eye grain patterns. But we usually work with straight-grained sugar maple.

Maple Wood FAQs
Learn more about maple wood as we try and answer some of the web's most frequently asked questions.
Is Maple Hard or Soft
Sugar Maple, the species we work with here at T.Y. Fine Furniture, is a hard, dense wood and a great choice for long-lasting pieces.
Other species of maple trees, such as Big Leaf Maple, Red Maple, and Silver Maple, produce soft timber. They’re still an excellent material for other wooden crafts but aren’t as durable when used to create furniture.
Can Maple Wood Be Used Outside
Maple isn’t the best material for decks and outdoor furniture. Other hardwoods like oak have a natural defense against moisture and insects. Maple doesn’t, and as such, it’s vulnerable to wood rot, decay, and insect attack.
You CAN use maple wood outside if that is your choice of material, but you might find using other hardwood more worthwhile.
How Long Does Maple Wood Last
Maple wood pieces are known for their durability, with an expected lifespan of 30 years and low maintenance requirements.
But premium sugar maple furniture lasts longer than 30 years, especially when crafted well and maintained with a high-caliber organic wood finish.
Which Maple Tree Is the Fastest Growing
The Red Maple is among the fastest-growing maple trees, increasing in height from 13 inches to more than 24 inches annually. It can take about 25 years before the Red Maple reaches its full mature height.
Other maple species with fast growth rates include Silver Maple and Bigtooth Maple.
Is Maple Wood Good Quality
Yes, sugar maple is a good quality hardwood.
Aside from their creamy color and beautiful grain pattern, sugar maples are often sought out for their strength and density. Furniture made from sugar maple can certainly withstand normal wear and tear and still look great for years.
Related Articles:
First published on May 23, 2022. This article has been updated.